What are Agency Rules and Regulations?
Federal Administrative Law
When Congress decides to regulate in a certain area, it will enact a statute which delegates the power to issue specific rules and regulations to an administrative agency that specializes in that area. In other words, when a law is passed by Congress, the law authorizes executive agencies to promulgate rules that interpret and fill in the administrative details of that law. These regulations have the force and effect of law.
Administrative law is a complicated category of law. Administrative law encompasses a wide assortment of materials, including the following:
- Executive orders, proclamations, and reorganization plans issued by the president.
- Rules and regulations issued by executive and independent agencies that have the force of statutory law.
- Administrative decisions made by administrative agencies.
The two main sources of administrative law are the Federal Register—a daily journal that records government agency regulations, proposed regulations, and public notices; and the Code of Federal Regulations—an annual compilation of regulations currently in force, arranged by subject matter. These sources also publish executive orders, proclamations, and reorganization plans issued by the president. Administrative decisions are typically published by the administrative agencies themselves in paper and/or on their websites.
Legal databases such as LexisNexis or Westlaw (or their student versions, Nexis Uni and Westlaw Campus Research) provide unofficial versions of administrative laws that are often more up to date, provide convenient, one-stop searching, and often include annotations and links to related materials.
The Federal Register: What It Is, and How to Use It is a tutorial sponsored by the Office of the Federal Register (OFR) and the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) to explain such topics as the historical background and legal basis of the Federal Register and Code of Federal Regulations, how the regulatory process works, and how to find information in print and online.
-
Regulations.govSearch for and make comments on pending regulations. This site even provides tips on writing an effective comment, and lets you make suggestions for areas that should be deregulated.
-
Federal RegisterThis official government journal publishes new executive and independent agency rules and regulations, proposed rules, and public notices. It also publishes executive orders and other presidential documents.
-
Code of Federal Regulations (Annual Edition)The Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) contains all regulations that were current at the time of publication, codified into 50 titles that represent broad subject areas.
The Federal Rulemaking Process
The Federal Rulemaking Process
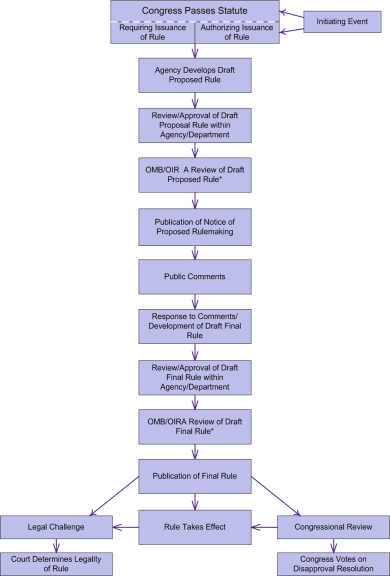
Source: The Federal Rulemaking Process: An Overview (CRS Report RL32240)
-
9 Steps in US Federal Rule Making ProcessThis brief article explains the federal rule-making process in layman's terms for easy understanding. The nine steps are as follows:
1. Initiating Events
2. Determination Where a Rule is Needed
3. Preparation of Proposed Rule
4. Office of Management and Budget (OMB) Review of Proposed Rule
5. Publication of Proposed Rule
6. Public Comments
7. Preparation of Final Rule, Interim Final Rule, Or Direct Final Rule
8. OMB Review of Final Rule, Interim Final Rule, or Direct Final Rule
9. Publication of Final Rule, Interim Final Rule, or Direct Final Rule -
An Overview of Federal Regulations and the Rulemaking ProcessThe purpose of this Congressional Research Service report is to provide members of Congress with an overview of the federal rulemaking process and a brief discussion of the major laws and executive orders that prescribe the procedures agencies are to apply when promulgating regulations.
-
The Informal Rulemaking ProcessThe informal rulemaking process, which often is referred to as “notice-and-comment rulemaking,” requires that an agency first issue a notice of proposed rulemaking (NPRM) and provide an opportunity for public comment on the proposal before it can issue a final rule. This is a simple summary of the most important elements of the legislative process, prepared by the U.S. Department of Transportation for individuals, small businesses, and others who do not participate in the process on a regular basis.
-
What Is Effective Commenting?Discover how to make comments that count—and maybe change the outcome! This explanation of how to make effective and persuasive comments on proposed rules comes from the Regulation Room, a now-defunct website that was sponsored by the National Science Foundation and Cornell Law School.
-
What is Rulemaking?Learn about the process that helps make the law—and that you have the right to be part of. This explanation of the rulemaking process comes from the Regulation Room, a now-defunct website that was sponsored by the National Science Foundation and Cornell Law School.
Finding a Federal Regulation
Citation to the Federal Register
A citation to the Federal Register contains four elements:
- A volume number
- The abbreviated title of the Federal Register (Fed. Reg.)
- The page number on which the cited regulation begins
- The date of the Federal Register issue in which the regulation appears.

"Federal Register Citation Example" by Westminster Law Library is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution—Non Commercial 4.0 International License.
Citation to the Code of Federal Regulations
A citation to the Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R.) contains four elements:
- The Title number
- C.F.R.— the abbreviation for Code of Federal Regulations
- The section number of the regulation
- The date of the edition of the C.F.R. that is being cited.

"Code of Federal Regulations Citation Example" by Westminster Law Library is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution—Non Commercial 4.0 International License.
Internet Resources and Databases
The main difference between the Federal Register and the Code of Federal Regulations is that the Code is a compilation of regulations that have been promulgated and have the force of law. The Register is a daily report of regulations that are working their way through the process of becoming finalized. For current regulations, search the Code of Federal Regulations. For proposed and pending regulations, search the Federal Register.
Federal Register—Online Editions
All proposed and final regulations are first published by the Government Printing Office (GPO) in chronological order in the Federal Register.
Free Websites
These government websites provide free access to the Federal Register.
-
GovInfo: Federal Register, 1936 to PresentPublished by the Office of the Federal Register, National Archives and Records Administration (NARA), the Federal Register is the official daily publication for rules, proposed rules, and notices of Federal agencies and organizations, as well as executive orders and other presidential documents. About the Federal Register
-
National Archives: Federal Register.govRecent issues of the Federal Register are available in PDF format or in a more user-friendly HTML format. Issues from before 1994 are not searchable but can be found with a Federal Register citation. This website includes many helpful resources, such as guides to using FederalRegister.gov, lists of popular documents, and tips on how to comment on Federal Register documents.
-
Regulations.gov: Your Voice in Federal DecisionmakingThis is a database of dockets and documents on federal regulatory actions. It includes not just rules and proposed rules, but also supporting and related material, comments, and other information such as complaints made to regulatory agencies. You can make your own comment on a proposed rule directly in this website, and tips are provided on how to make your comment more persuasive.
Subscription Databases
-
HeinOnline Federal Register Library, 1936–PresentDaily issues of the Federal Register are browsable by day back to 1936, when the first issue was published. Indexing to the section level of the Federal Register is available for 1995 to the present.
-
Nexis Uni: Federal Register, 1936–PresentFederal Register (FEDREG) contains the full text of all documents that are published in the Federal Register. Documents from June 1979 to March 1936 are available in PDF format. Additionally, while these documents do not display in full-text, they are searched in natural language queries and will return with results. However, they are not searched with Boolean language searches.
Code of Federal Regulations—Online Editions
Next, regulations are then codified by subject in the Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R.). The C.F.R. is organized in to 50 broad subject titles, and is revised annually.
Free Websites
These government websites provide free access to the <i>Code of Federal Regulations</i>. They vary in years covered and how up to date they are.
-
GovInfo.gov: Code of Federal Regulations (Annual Edition), 1996–presentThe Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) contains all regulations that were current at the time of publication, codified into 50 titles that represent broad subject areas.
-
Library of Congress: Code of Federal Regulations, 1938–1995The Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R.) is "the codification of the general and permanent rules by the department and agencies of the Federal Government." This is a historical collection of the Code of Federal Regulations dating from inception (1938) to 1995.
-
Electronic Code of Federal Regulations (eCFR)The Electronic Code of Federal Regulations (eCFR) is a an online version of the CFR that is updated daily to stay current. The eCFR is an editorial compilation of CFR material and amendments published in the daily Federal Register. It is not an official legal edition of the CFR.
Subscription Databases
These databases are available to the UNT community and to visitors at the UNT campus.
-
HeinOnline: Code of Federal Regulations (1938–current)HeinOnline provides comprehensive coverage of the Code of Federal Regulations, with more than 8,500 volumes dating back to inception (1938)
-
Nexis Uni: Code of Federal Regulations (9/13/2012 to present)The CFR - Code of Federal Regulations file in Nexis Uni contains the full text of all titles from the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). The CFR is a codification of the general and permanent rules and regulations published originally in the Federal Register by executive departments and agencies of the federal government. CFR archives are available from 1981.